|
Prusa MINI Firmware overview
|
|
| #define | GCC_STRICT_OVERFLOW 0 |
| |
| #define | APPEND_STRING(string) pos = png_safecat(out, 29, pos, (string)) |
| |
| #define | APPEND_NUMBER(format, value) APPEND_STRING(PNG_FORMAT_NUMBER(number_buf, format, (value))) |
| |
| #define | APPEND(ch) if (pos < 28) out[pos++] = (ch) |
| |
| #define | PNG_MD5(a, b, c, d) { a, b, c, d }, (a!=0)||(b!=0)||(c!=0)||(d!=0) |
| |
| #define | PNG_ICC_CHECKSUM(adler, crc, md5, intent, broke, date, length, fname) { adler, crc, length, md5, broke, intent }, |
| |
| #define | png_gt(a, b) ((a) > (b)) |
| |
| #define | png_fp_add(state, flags) ((state) |= (flags)) |
| |
| #define | png_fp_set(state, value) ((state) = (value) | ((state) & PNG_FP_STICKY)) |
| |
|
| void PNGAPI | png_set_sig_bytes (png_structrp png_ptr, int num_bytes) |
| |
| int PNGAPI | png_sig_cmp (png_const_bytep sig, size_t start, size_t num_to_check) |
| |
| | PNG_FUNCTION (voidpf, png_zalloc,(voidpf png_ptr, uInt items, uInt size), PNG_ALLOCATED) |
| |
| void | png_zfree (voidpf png_ptr, voidpf ptr) |
| |
| void | png_reset_crc (png_structrp png_ptr) |
| |
| void | png_calculate_crc (png_structrp png_ptr, png_const_bytep ptr, size_t length) |
| |
| int | png_user_version_check (png_structrp png_ptr, png_const_charp user_png_ver) |
| |
| | PNG_FUNCTION (png_structp, png_create_png_struct,(png_const_charp user_png_ver, png_voidp error_ptr, png_error_ptr error_fn, png_error_ptr warn_fn, png_voidp mem_ptr, png_malloc_ptr malloc_fn, png_free_ptr free_fn), PNG_ALLOCATED) |
| |
| | PNG_FUNCTION (png_infop, PNGAPI png_create_info_struct,(png_const_structrp png_ptr), PNG_ALLOCATED) |
| |
| void PNGAPI | png_destroy_info_struct (png_const_structrp png_ptr, png_infopp info_ptr_ptr) |
| |
| | PNG_FUNCTION (void, PNGAPI png_info_init_3,(png_infopp ptr_ptr, size_t png_info_struct_size), PNG_DEPRECATED) |
| |
| void PNGAPI | png_data_freer (png_const_structrp png_ptr, png_inforp info_ptr, int freer, png_uint_32 mask) |
| |
| void PNGAPI | png_free_data (png_const_structrp png_ptr, png_inforp info_ptr, png_uint_32 mask, int num) |
| |
| png_voidp PNGAPI | png_get_io_ptr (png_const_structrp png_ptr) |
| |
| void PNGAPI | png_init_io (png_structrp png_ptr, png_FILE_p fp) |
| |
| void PNGAPI | png_save_int_32 (png_bytep buf, png_int_32 i) |
| |
| int PNGAPI | png_convert_to_rfc1123_buffer (char out[29], png_const_timep ptime) |
| |
| png_const_charp PNGAPI | png_convert_to_rfc1123 (png_structrp png_ptr, png_const_timep ptime) |
| |
| png_const_charp PNGAPI | png_get_copyright (png_const_structrp png_ptr) |
| |
| png_const_charp PNGAPI | png_get_libpng_ver (png_const_structrp png_ptr) |
| |
| png_const_charp PNGAPI | png_get_header_ver (png_const_structrp png_ptr) |
| |
| png_const_charp PNGAPI | png_get_header_version (png_const_structrp png_ptr) |
| |
| void PNGAPI | png_build_grayscale_palette (int bit_depth, png_colorp palette) |
| |
| int PNGAPI | png_handle_as_unknown (png_const_structrp png_ptr, png_const_bytep chunk_name) |
| |
| int | png_chunk_unknown_handling (png_const_structrp png_ptr, png_uint_32 chunk_name) |
| |
| int PNGAPI | png_reset_zstream (png_structrp png_ptr) |
| |
| png_uint_32 PNGAPI | png_access_version_number (void) |
| |
| void | png_zstream_error (png_structrp png_ptr, int ret) |
| |
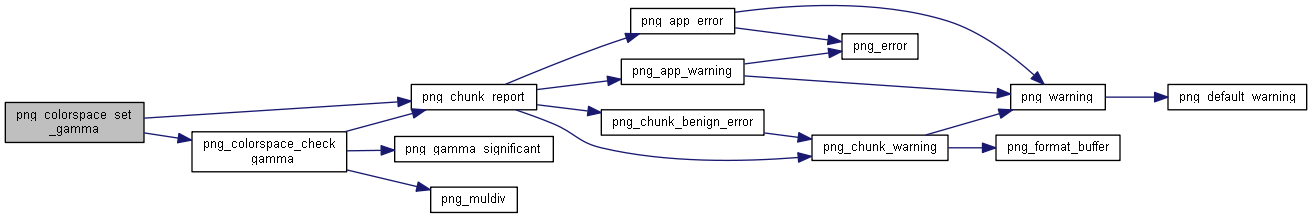
| static int | png_colorspace_check_gamma (png_const_structrp png_ptr, png_colorspacerp colorspace, png_fixed_point gAMA, int from) |
| |
| void | png_colorspace_set_gamma (png_const_structrp png_ptr, png_colorspacerp colorspace, png_fixed_point gAMA) |
| |
| void | png_colorspace_sync_info (png_const_structrp png_ptr, png_inforp info_ptr) |
| |
| void | png_colorspace_sync (png_const_structrp png_ptr, png_inforp info_ptr) |
| |
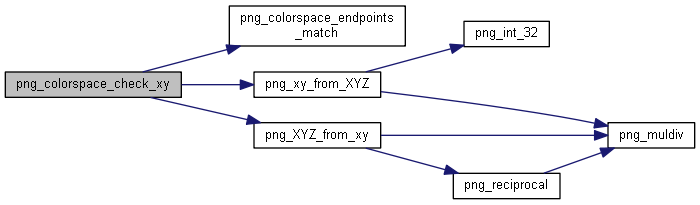
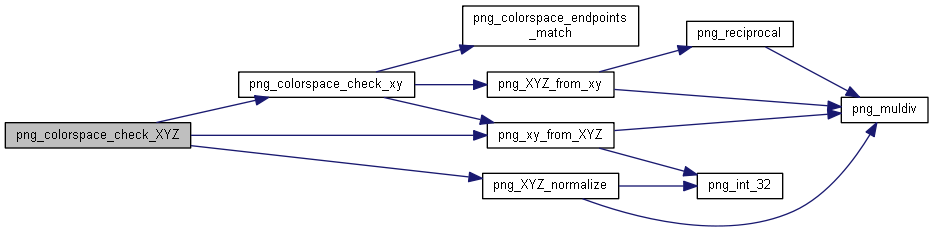
| static int | png_xy_from_XYZ (png_xy *xy, const png_XYZ *XYZ) |
| |
| static int | png_XYZ_from_xy (png_XYZ *XYZ, const png_xy *xy) |
| |
| static int | png_XYZ_normalize (png_XYZ *XYZ) |
| |
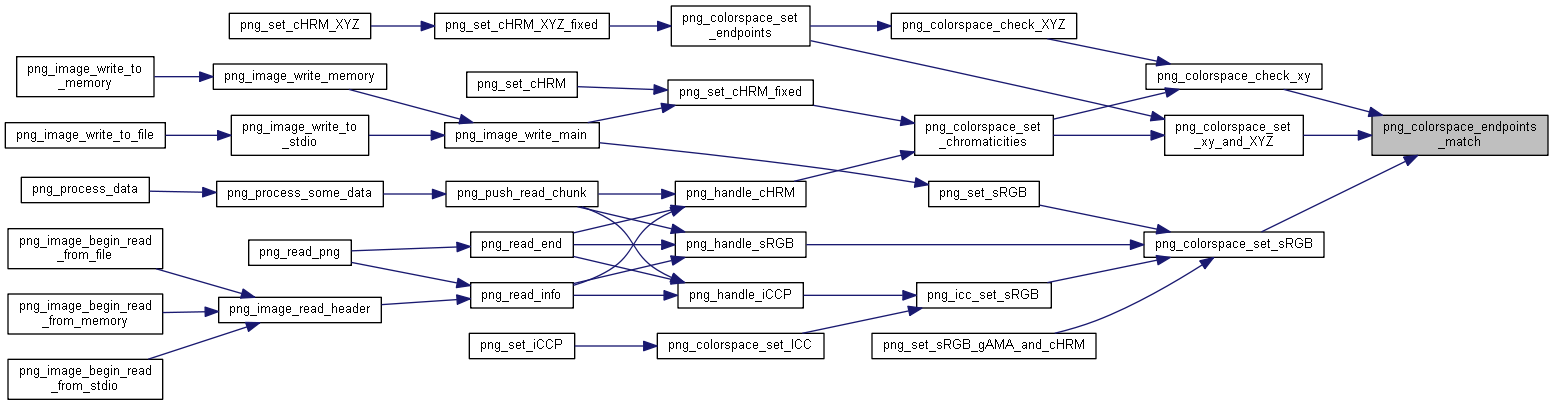
| static int | png_colorspace_endpoints_match (const png_xy *xy1, const png_xy *xy2, int delta) |
| |
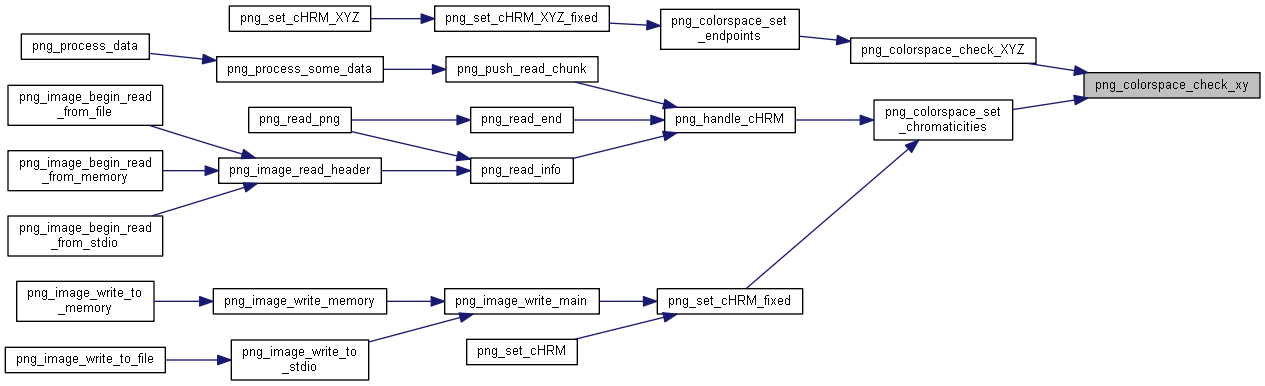
| static int | png_colorspace_check_xy (png_XYZ *XYZ, const png_xy *xy) |
| |
| static int | png_colorspace_check_XYZ (png_xy *xy, png_XYZ *XYZ) |
| |
| static int | png_colorspace_set_xy_and_XYZ (png_const_structrp png_ptr, png_colorspacerp colorspace, const png_xy *xy, const png_XYZ *XYZ, int preferred) |
| |
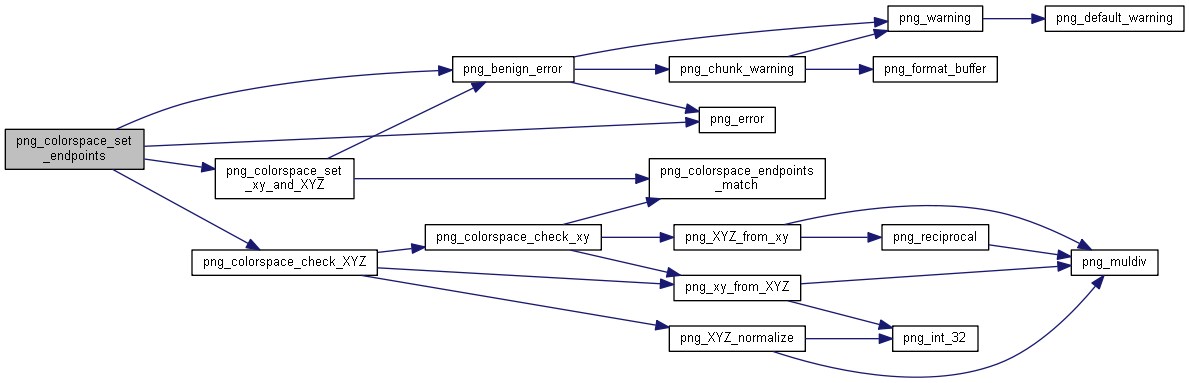
| int | png_colorspace_set_chromaticities (png_const_structrp png_ptr, png_colorspacerp colorspace, const png_xy *xy, int preferred) |
| |
| int | png_colorspace_set_endpoints (png_const_structrp png_ptr, png_colorspacerp colorspace, const png_XYZ *XYZ_in, int preferred) |
| |
| static char | png_icc_tag_char (png_uint_32 byte) |
| |
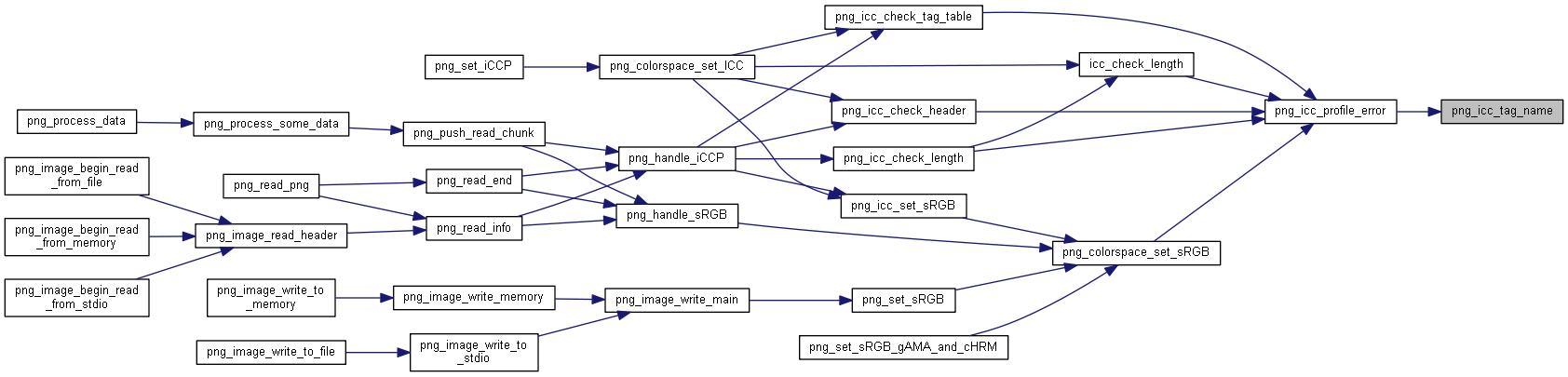
| static void | png_icc_tag_name (char *name, png_uint_32 tag) |
| |
| static int | is_ICC_signature_char (png_alloc_size_t it) |
| |
| static int | is_ICC_signature (png_alloc_size_t it) |
| |
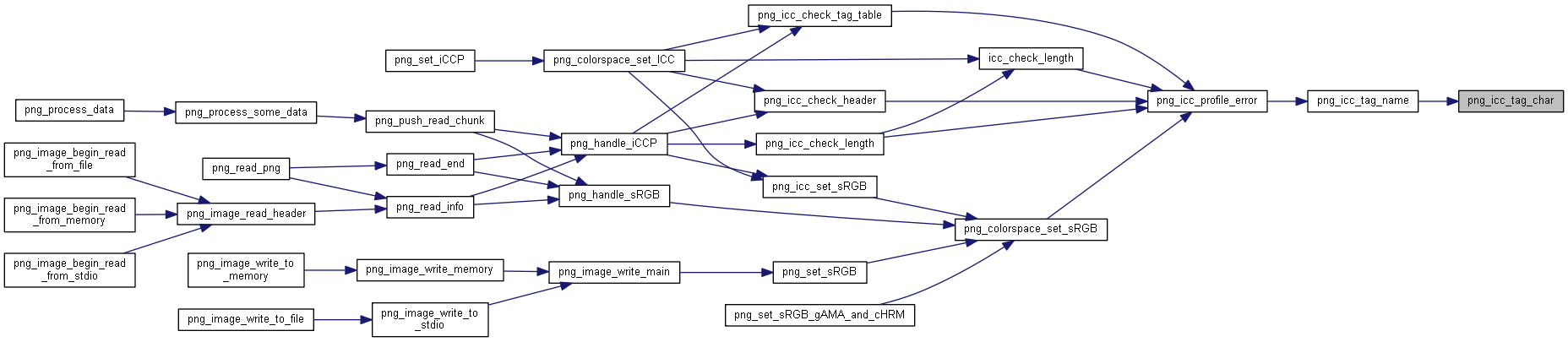
| static int | png_icc_profile_error (png_const_structrp png_ptr, png_colorspacerp colorspace, png_const_charp name, png_alloc_size_t value, png_const_charp reason) |
| |
| int | png_colorspace_set_sRGB (png_const_structrp png_ptr, png_colorspacerp colorspace, int intent) |
| |
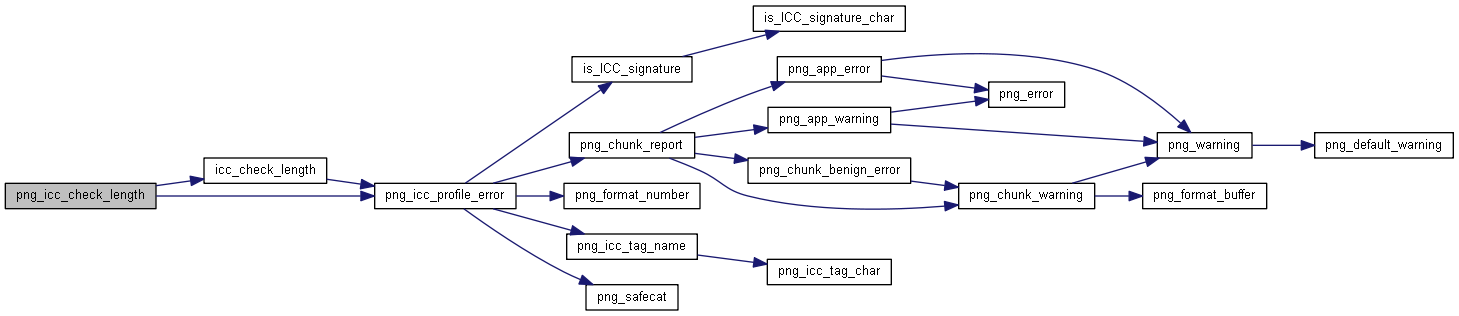
| static int | icc_check_length (png_const_structrp png_ptr, png_colorspacerp colorspace, png_const_charp name, png_uint_32 profile_length) |
| |
| int | png_icc_check_length (png_const_structrp png_ptr, png_colorspacerp colorspace, png_const_charp name, png_uint_32 profile_length) |
| |
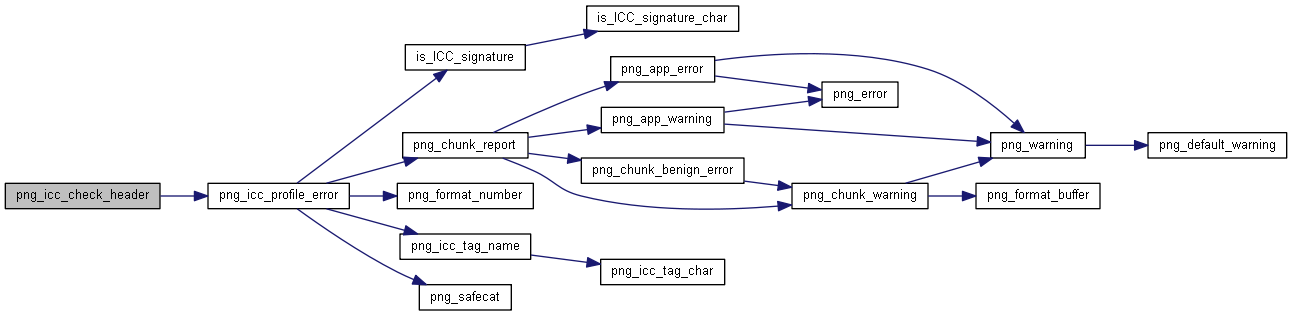
| int | png_icc_check_header (png_const_structrp png_ptr, png_colorspacerp colorspace, png_const_charp name, png_uint_32 profile_length, png_const_bytep profile, int color_type) |
| |
| int | png_icc_check_tag_table (png_const_structrp png_ptr, png_colorspacerp colorspace, png_const_charp name, png_uint_32 profile_length, png_const_bytep profile) |
| |
| static int | png_compare_ICC_profile_with_sRGB (png_const_structrp png_ptr, png_const_bytep profile, uLong adler) |
| |
| void | png_icc_set_sRGB (png_const_structrp png_ptr, png_colorspacerp colorspace, png_const_bytep profile, uLong adler) |
| |
| int | png_colorspace_set_ICC (png_const_structrp png_ptr, png_colorspacerp colorspace, png_const_charp name, png_uint_32 profile_length, png_const_bytep profile, int color_type) |
| |
| void | png_colorspace_set_rgb_coefficients (png_structrp png_ptr) |
| |
| void | png_check_IHDR (png_const_structrp png_ptr, png_uint_32 width, png_uint_32 height, int bit_depth, int color_type, int interlace_type, int compression_type, int filter_type) |
| |
| int | png_check_fp_number (png_const_charp string, size_t size, int *statep, png_size_tp whereami) |
| |
| int | png_check_fp_string (png_const_charp string, size_t size) |
| |
| static double | png_pow10 (int power) |
| |
| void | png_ascii_from_fp (png_const_structrp png_ptr, png_charp ascii, size_t size, double fp, unsigned int precision) |
| |
| void | png_ascii_from_fixed (png_const_structrp png_ptr, png_charp ascii, size_t size, png_fixed_point fp) |
| |
| png_fixed_point | png_fixed (png_const_structrp png_ptr, double fp, png_const_charp text) |
| |
| int | png_muldiv (png_fixed_point_p res, png_fixed_point a, png_int_32 times, png_int_32 divisor) |
| |
| png_fixed_point | png_muldiv_warn (png_const_structrp png_ptr, png_fixed_point a, png_int_32 times, png_int_32 divisor) |
| |
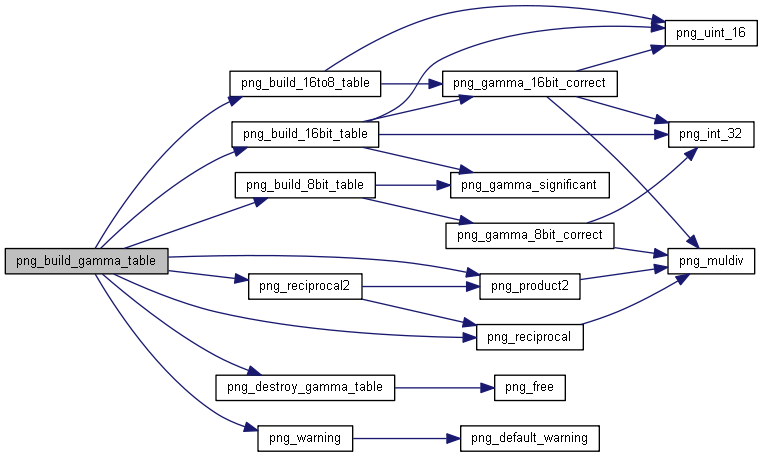
| png_fixed_point | png_reciprocal (png_fixed_point a) |
| |
| int | png_gamma_significant (png_fixed_point gamma_val) |
| |
| static png_fixed_point | png_product2 (png_fixed_point a, png_fixed_point b) |
| |
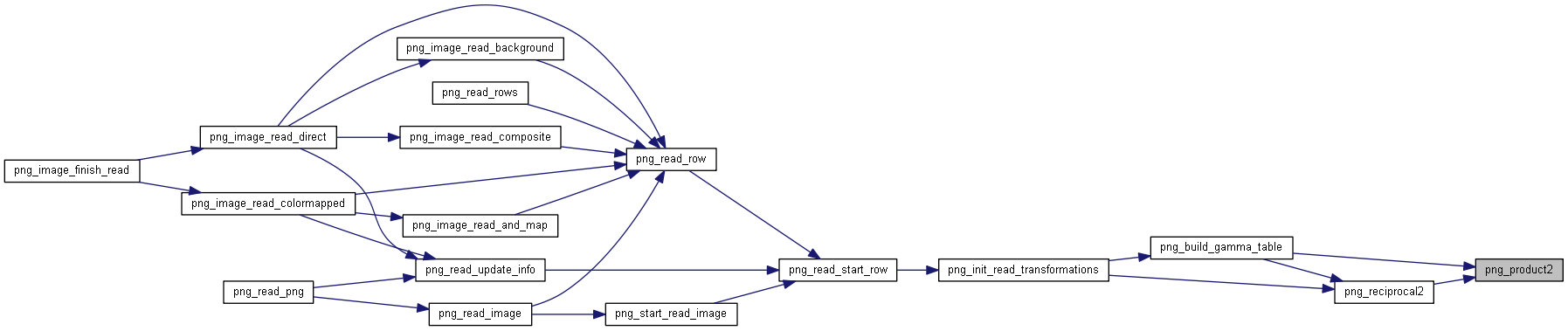
| png_fixed_point | png_reciprocal2 (png_fixed_point a, png_fixed_point b) |
| |
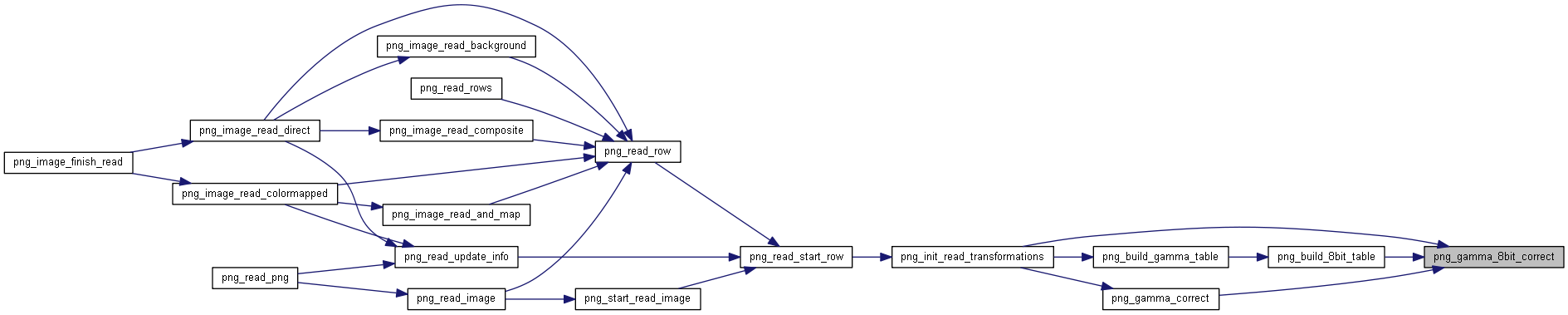
| png_byte | png_gamma_8bit_correct (unsigned int value, png_fixed_point gamma_val) |
| |
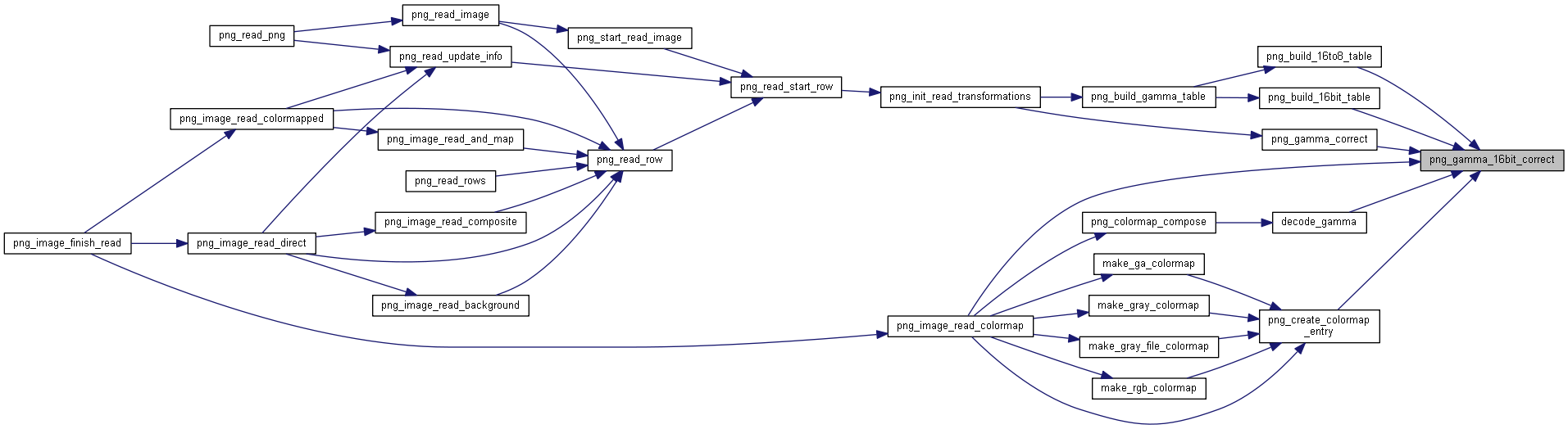
| png_uint_16 | png_gamma_16bit_correct (unsigned int value, png_fixed_point gamma_val) |
| |
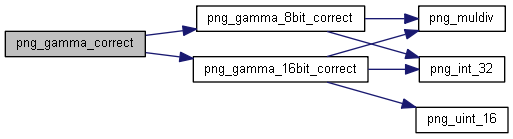
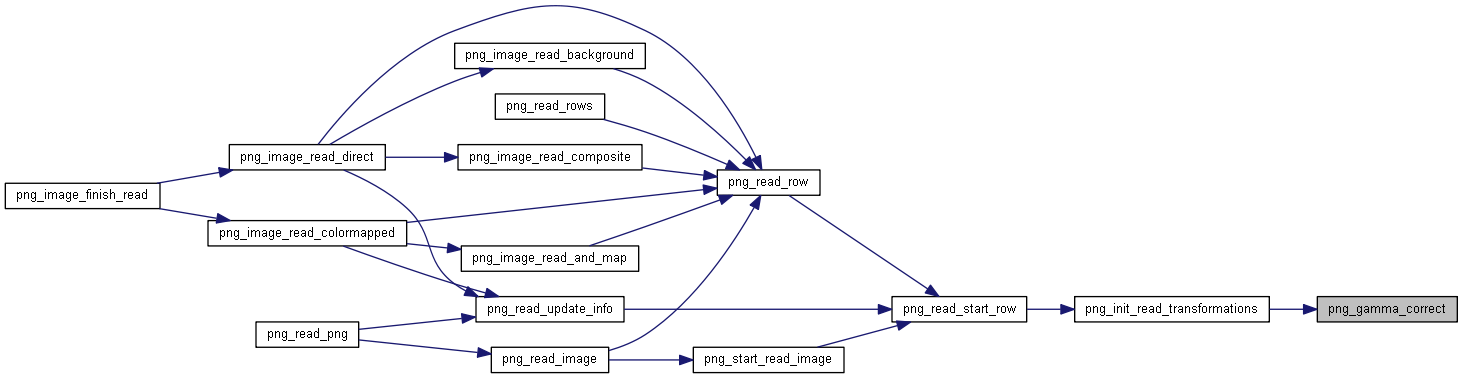
| png_uint_16 | png_gamma_correct (png_structrp png_ptr, unsigned int value, png_fixed_point gamma_val) |
| |
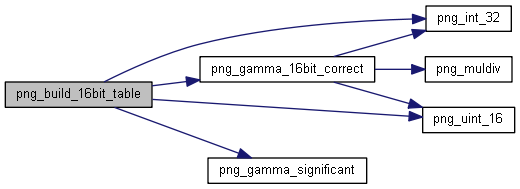
| static void | png_build_16bit_table (png_structrp png_ptr, png_uint_16pp *ptable, unsigned int shift, png_fixed_point gamma_val) |
| |
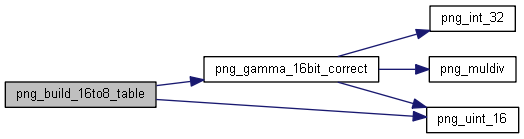
| static void | png_build_16to8_table (png_structrp png_ptr, png_uint_16pp *ptable, unsigned int shift, png_fixed_point gamma_val) |
| |
| static void | png_build_8bit_table (png_structrp png_ptr, png_bytepp ptable, png_fixed_point gamma_val) |
| |
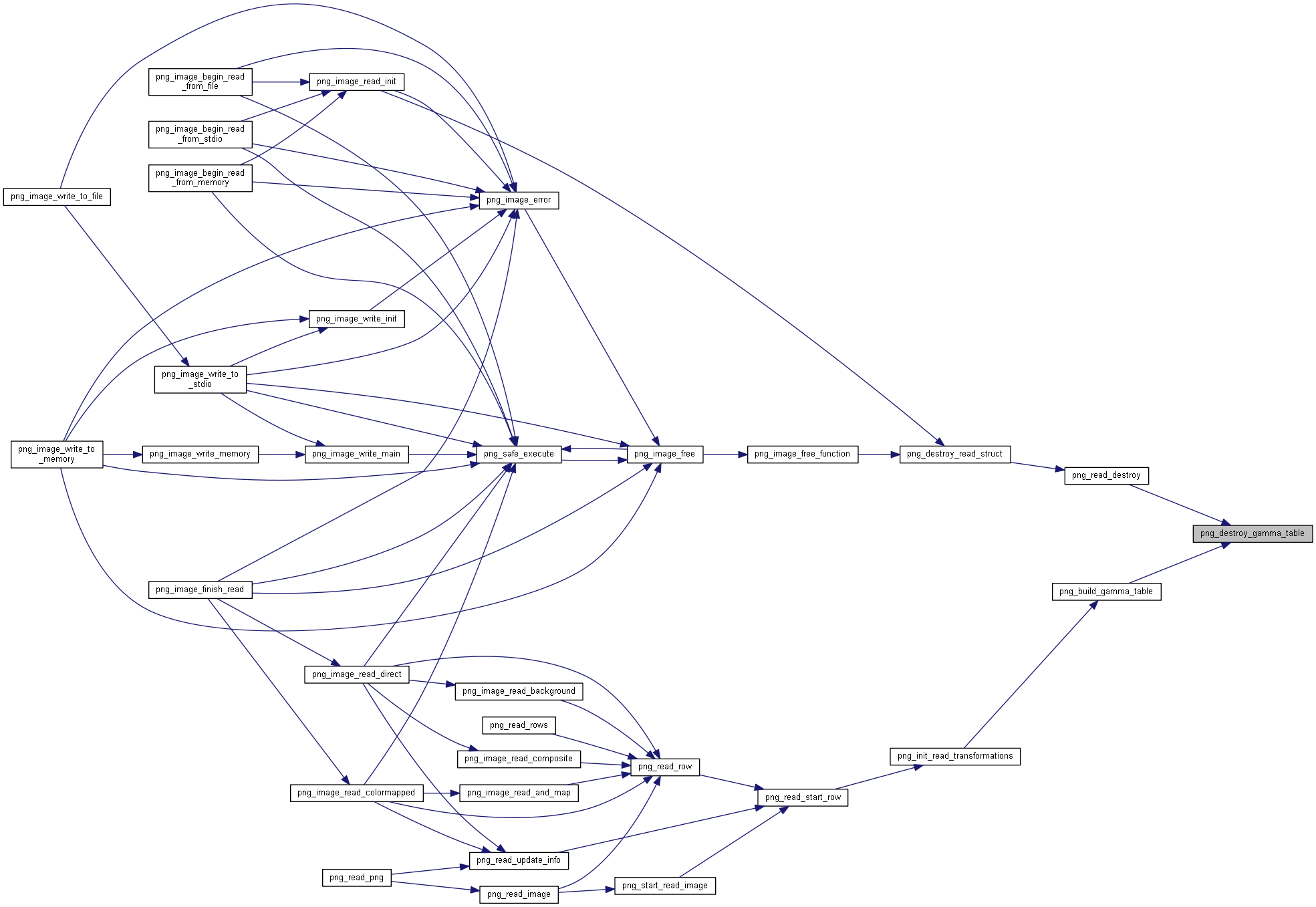
| void | png_destroy_gamma_table (png_structrp png_ptr) |
| |
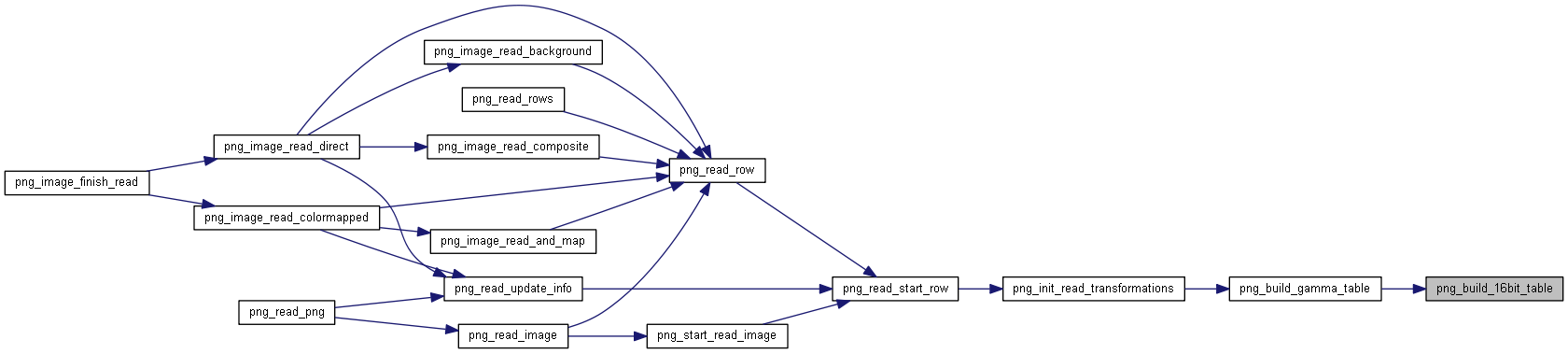
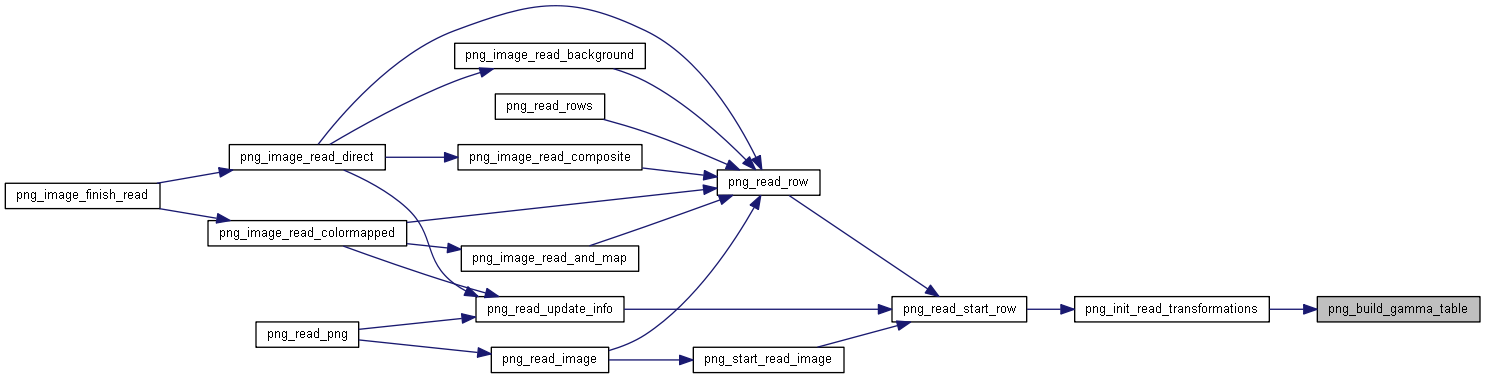
| void | png_build_gamma_table (png_structrp png_ptr, int bit_depth) |
| |
| int PNGAPI | png_set_option (png_structrp png_ptr, int option, int onoff) |
| |
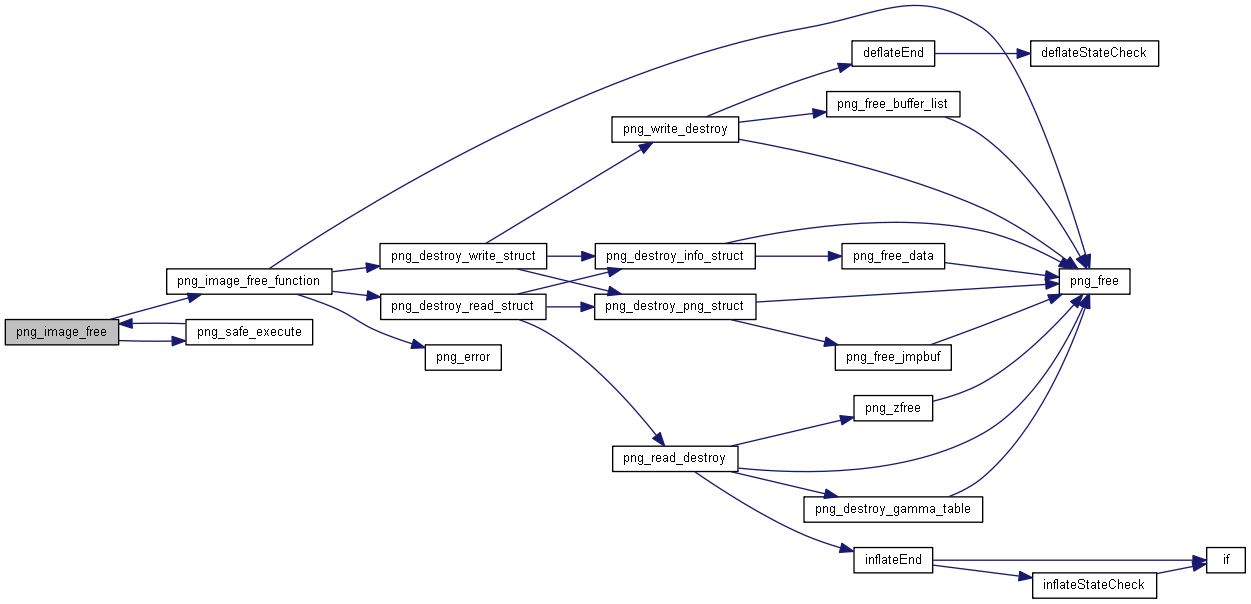
| static int | png_image_free_function (png_voidp argument) |
| |
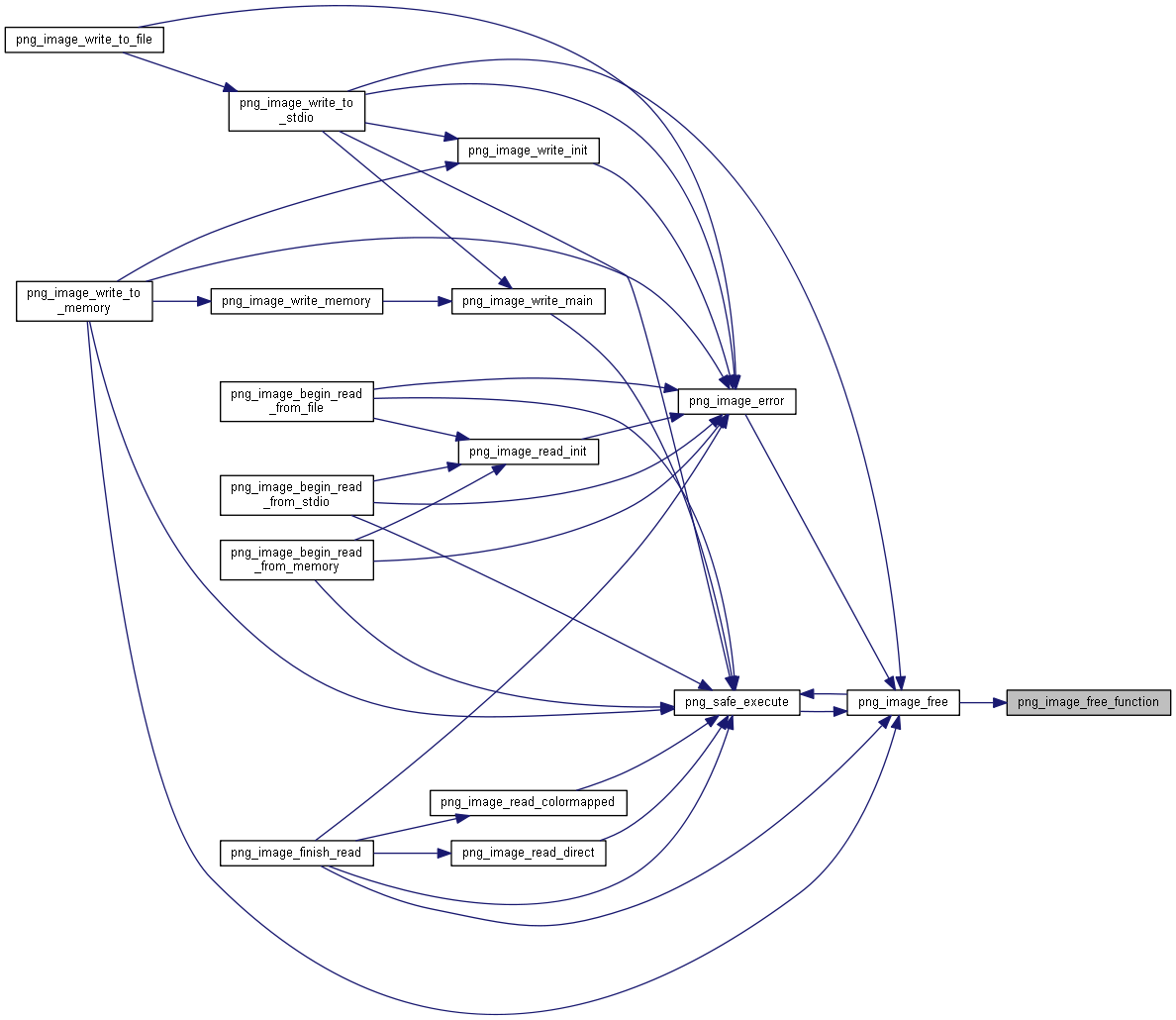
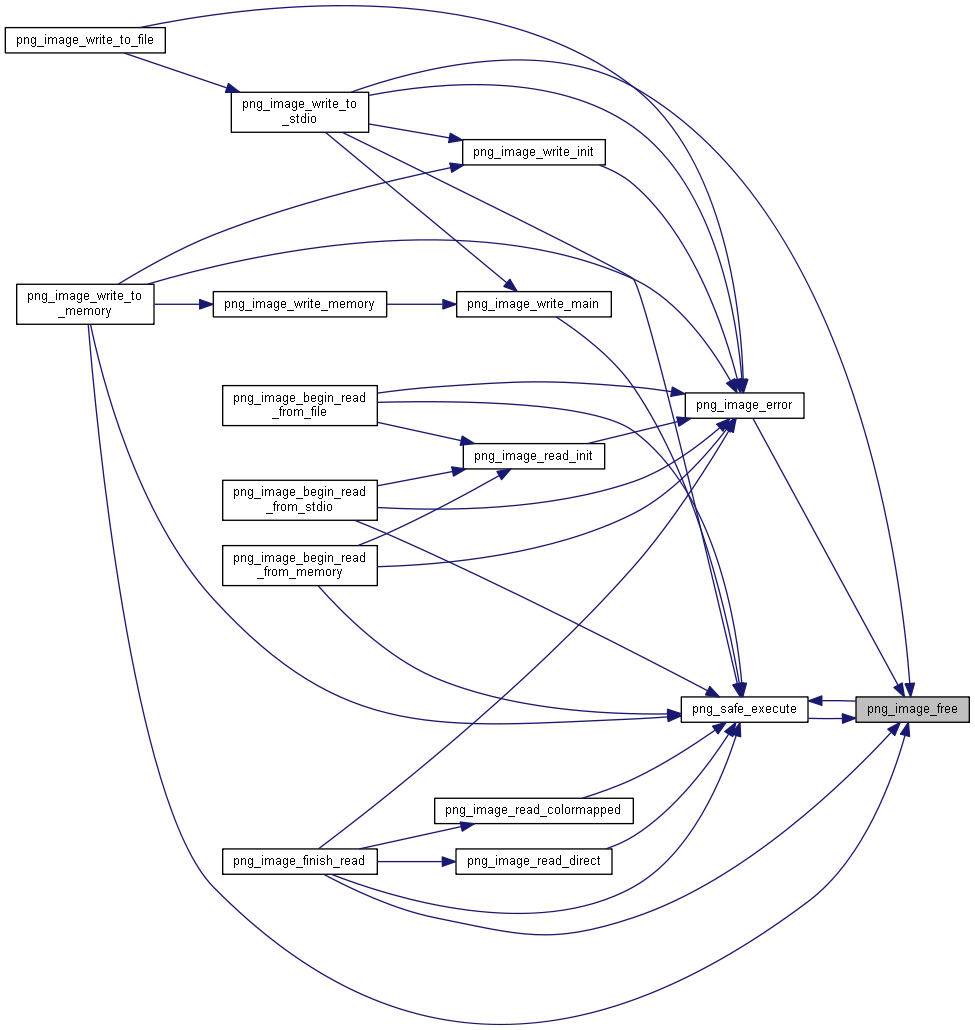
| void PNGAPI | png_image_free (png_imagep image) |
| |
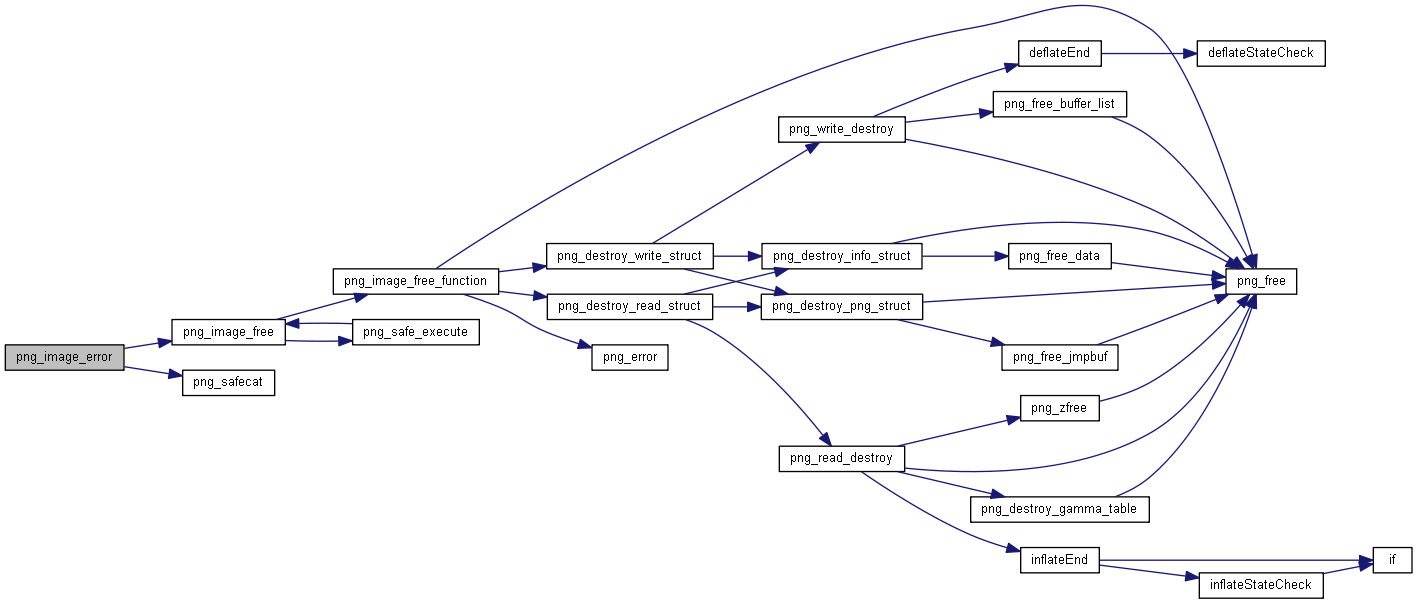
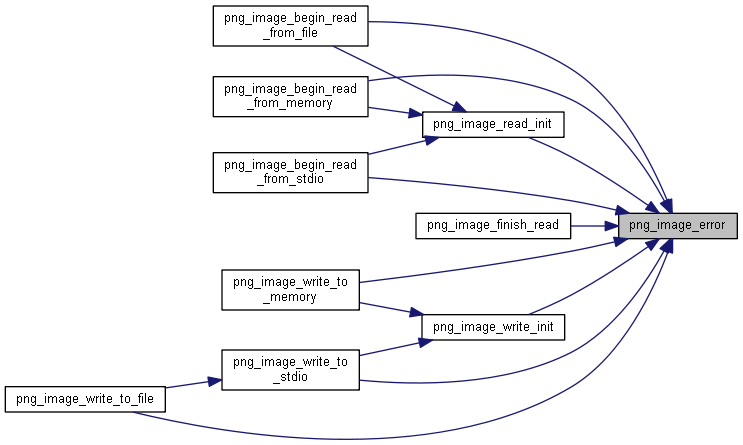
| int | png_image_error (png_imagep image, png_const_charp error_message) |
| |
◆ GCC_STRICT_OVERFLOW
| #define GCC_STRICT_OVERFLOW 0 |
◆ APPEND_STRING
| #define APPEND_STRING |
( |
|
string | ) |
pos = png_safecat(out, 29, pos, (string)) |
◆ APPEND_NUMBER
◆ APPEND
| #define APPEND |
( |
|
ch | ) |
if (pos < 28) out[pos++] = (ch) |
◆ PNG_MD5
| #define PNG_MD5 |
( |
|
a, |
|
|
|
b, |
|
|
|
c, |
|
|
|
d |
|
) |
| { a, b, c, d }, (a!=0)||(b!=0)||(c!=0)||(d!=0) |
◆ PNG_ICC_CHECKSUM
| #define PNG_ICC_CHECKSUM |
( |
|
adler, |
|
|
|
crc, |
|
|
|
md5, |
|
|
|
intent, |
|
|
|
broke, |
|
|
|
date, |
|
|
|
length, |
|
|
|
fname |
|
) |
| { adler, crc, length, md5, broke, intent }, |
◆ png_gt
| #define png_gt |
( |
|
a, |
|
|
|
b |
|
) |
| ((a) > (b)) |
◆ png_fp_add
| #define png_fp_add |
( |
|
state, |
|
|
|
flags |
|
) |
| ((state) |= (flags)) |
◆ png_fp_set
◆ Your_png_h_is_not_version_1_6_36
◆ png_set_sig_bytes()
49 unsigned int nb = (
unsigned int)num_bytes;
62 png_ptr->sig_bytes = (png_byte)nb;
◆ png_sig_cmp()
76 png_byte png_signature[8] = {137, 80, 78, 71, 13, 10, 26, 10};
81 else if (num_to_check < 1)
87 if (
start + num_to_check > 8)
88 num_to_check = 8 -
start;
90 return ((
int)(memcmp(&sig[
start], &png_signature[
start], num_to_check)));
◆ PNG_FUNCTION() [1/4]
108 "Potential overflow in png_zalloc()");
◆ png_zfree()
◆ png_reset_crc()
◆ png_calculate_crc()
161 if (need_crc != 0 &&
length > 0)
169 if (safe_length == 0)
170 safe_length = (
uInt)-1;
◆ png_user_version_check()
200 if (user_png_ver !=
NULL)
210 if (user_png_ver[
i] ==
'.')
212 }
while (found_dots < 2 && user_png_ver[
i] != 0 &&
221 #ifdef PNG_WARNINGS_SUPPORTED
226 "Application built with libpng-");
227 pos =
png_safecat(m, (
sizeof m), pos, user_png_ver);
228 pos =
png_safecat(m, (
sizeof m), pos,
" but running with ");
235 #ifdef PNG_ERROR_NUMBERS_SUPPORTED
◆ PNG_FUNCTION() [2/4]
255 # ifdef PNG_SETJMP_SUPPORTED
256 jmp_buf create_jmp_buf;
263 memset(&create_struct, 0, (
sizeof create_struct));
266 # ifdef PNG_USER_LIMITS_SUPPORTED
270 # ifdef PNG_USER_CHUNK_CACHE_MAX
275 # ifdef PNG_USER_CHUNK_MALLOC_MAX
286 # ifdef PNG_USER_MEM_SUPPORTED
301 # ifdef PNG_SETJMP_SUPPORTED
302 if (!setjmp(create_jmp_buf))
305 # ifdef PNG_SETJMP_SUPPORTED
311 create_struct.jmp_buf_ptr = &create_jmp_buf;
312 create_struct.jmp_buf_size = 0;
313 create_struct.longjmp_fn = longjmp;
320 png_malloc_warn(&create_struct, (
sizeof *
png_ptr)));
331 # ifdef PNG_SETJMP_SUPPORTED
333 create_struct.jmp_buf_ptr =
NULL;
334 create_struct.jmp_buf_size = 0;
335 create_struct.longjmp_fn = 0;
◆ PNG_FUNCTION() [3/4]
358 png_debug(1,
"in png_create_info_struct");
◆ png_destroy_info_struct()
390 png_debug(1,
"in png_destroy_info_struct");
395 if (info_ptr_ptr !=
NULL)
406 *info_ptr_ptr =
NULL;
◆ PNG_FUNCTION() [4/4]
434 if ((
sizeof (
png_info)) > png_info_struct_size)
◆ png_data_freer()
◆ png_free_data()
479 #ifdef PNG_TEXT_SUPPORTED
505 #ifdef PNG_tRNS_SUPPORTED
516 #ifdef PNG_sCAL_SUPPORTED
528 #ifdef PNG_pCAL_SUPPORTED
551 #ifdef PNG_iCCP_SUPPORTED
563 #ifdef PNG_sPLT_SUPPORTED
594 #ifdef PNG_STORE_UNKNOWN_CHUNKS_SUPPORTED
618 #ifdef PNG_eXIf_SUPPORTED
622 # ifdef PNG_READ_eXIf_SUPPORTED
638 #ifdef PNG_hIST_SUPPORTED
657 #ifdef PNG_INFO_IMAGE_SUPPORTED
664 for (row = 0; row <
info_ptr->height; row++)
◆ png_get_io_ptr()
◆ png_init_io()
◆ png_save_int_32()
◆ png_convert_to_rfc1123_buffer()
739 static const char short_months[12][4] =
740 {
"Jan",
"Feb",
"Mar",
"Apr",
"May",
"Jun",
741 "Jul",
"Aug",
"Sep",
"Oct",
"Nov",
"Dec"};
746 if (ptime->year > 9999 ||
747 ptime->month == 0 || ptime->month > 12 ||
748 ptime->day == 0 || ptime->day > 31 ||
749 ptime->hour > 23 || ptime->minute > 59 ||
757 # define APPEND_STRING(string) pos = png_safecat(out, 29, pos, (string))
758 # define APPEND_NUMBER(format, value)\
759 APPEND_STRING(PNG_FORMAT_NUMBER(number_buf, format, (value)))
760 # define APPEND(ch) if (pos < 28) out[pos++] = (ch)
777 # undef APPEND_NUMBER
778 # undef APPEND_STRING
◆ png_convert_to_rfc1123()
◆ png_get_copyright()
814 #ifdef PNG_STRING_COPYRIGHT
815 return PNG_STRING_COPYRIGHT
820 "Copyright (c) 1998-2002,2004,2006-2018 Glenn Randers-Pehrson" \
823 "Copyright (c) 1995-1996 Guy Eric Schalnat, Group 42, Inc." \
◆ png_get_libpng_ver()
◆ png_get_header_ver()
◆ png_get_header_version()
858 # ifndef PNG_READ_SUPPORTED
◆ png_build_grayscale_palette()
882 png_debug(1,
"in png_do_build_grayscale_palette");
915 for (
i = 0, v = 0;
i < num_palette;
i++, v += color_inc)
917 palette[
i].
red = (png_byte)(v & 0xff);
918 palette[
i].
green = (png_byte)(v & 0xff);
919 palette[
i].
blue = (png_byte)(v & 0xff);
◆ png_handle_as_unknown()
935 p = p_end +
png_ptr->num_chunk_list*5;
945 if (memcmp(chunk_name, p, 4) == 0)
◆ png_chunk_unknown_handling()
963 png_byte chunk_string[5];
◆ png_reset_zstream()
◆ png_access_version_number()
◆ png_zstream_error()
◆ png_colorspace_check_gamma()
1084 if ((colorspace->flags & PNG_COLORSPACE_HAVE_GAMMA) != 0 &&
1094 if ((colorspace->flags & PNG_COLORSPACE_FROM_sRGB) != 0 || from == 2)
◆ png_colorspace_set_gamma()
1130 if (gAMA < 16 || gAMA > 625000000)
1131 errmsg =
"gamma value out of range";
1133 # ifdef PNG_READ_gAMA_SUPPORTED
1136 (colorspace->flags & PNG_COLORSPACE_FROM_gAMA) != 0)
1137 errmsg =
"duplicate";
1141 else if ((colorspace->flags & PNG_COLORSPACE_INVALID) != 0)
1150 colorspace->gamma = gAMA;
1151 colorspace->flags |=
1152 (PNG_COLORSPACE_HAVE_GAMMA | PNG_COLORSPACE_FROM_gAMA);
1164 colorspace->flags |= PNG_COLORSPACE_INVALID;
◆ png_colorspace_sync_info()
1171 if ((
info_ptr->colorspace.flags & PNG_COLORSPACE_INVALID) != 0)
1177 # ifdef PNG_COLORSPACE_SUPPORTED
1187 # ifdef PNG_COLORSPACE_SUPPORTED
1192 if ((
info_ptr->colorspace.flags & PNG_COLORSPACE_MATCHES_sRGB) != 0)
1198 if ((
info_ptr->colorspace.flags & PNG_COLORSPACE_HAVE_ENDPOINTS) != 0)
1205 if ((
info_ptr->colorspace.flags & PNG_COLORSPACE_HAVE_GAMMA) != 0)
◆ png_colorspace_sync()
◆ png_xy_from_XYZ()
| static int png_xy_from_XYZ |
( |
png_xy * |
xy, |
|
|
const png_XYZ * |
XYZ |
|
) |
| |
|
static |
1237 d =
XYZ->red_X +
XYZ->red_Y +
XYZ->red_Z;
1243 whiteX =
XYZ->red_X;
1244 whiteY =
XYZ->red_Y;
1246 d =
XYZ->green_X +
XYZ->green_Y +
XYZ->green_Z;
1252 whiteX +=
XYZ->green_X;
1253 whiteY +=
XYZ->green_Y;
1255 d =
XYZ->blue_X +
XYZ->blue_Y +
XYZ->blue_Z;
1261 whiteX +=
XYZ->blue_X;
1262 whiteY +=
XYZ->blue_Y;
◆ png_XYZ_from_xy()
| static int png_XYZ_from_xy |
( |
png_XYZ * |
XYZ, |
|
|
const png_xy * |
xy |
|
) |
| |
|
static |
1286 if (xy->redx < 0 || xy->redx >
PNG_FP_1)
return 1;
1287 if (xy->redy < 0 || xy->redy >
PNG_FP_1-xy->redx)
return 1;
1288 if (xy->greenx < 0 || xy->greenx >
PNG_FP_1)
return 1;
1289 if (xy->greeny < 0 || xy->greeny >
PNG_FP_1-xy->greenx)
return 1;
1290 if (xy->bluex < 0 || xy->bluex >
PNG_FP_1)
return 1;
1291 if (xy->bluey < 0 || xy->bluey >
PNG_FP_1-xy->bluex)
return 1;
1292 if (xy->whitex < 0 || xy->whitex >
PNG_FP_1)
return 1;
1293 if (xy->whitey < 5 || xy->whitey >
PNG_FP_1-xy->whitex)
return 1;
1474 if (
png_muldiv(&left, xy->greenx-xy->bluex, xy->redy - xy->bluey, 7) == 0)
1476 if (
png_muldiv(&right, xy->greeny-xy->bluey, xy->redx - xy->bluex, 7) == 0)
1478 denominator = left - right;
1481 if (
png_muldiv(&left, xy->greenx-xy->bluex, xy->whitey-xy->bluey, 7) == 0)
1483 if (
png_muldiv(&right, xy->greeny-xy->bluey, xy->whitex-xy->bluex, 7) == 0)
1491 if (
png_muldiv(&red_inverse, xy->whitey, denominator, left-right) == 0 ||
1492 red_inverse <= xy->whitey )
1496 if (
png_muldiv(&left, xy->redy-xy->bluey, xy->whitex-xy->bluex, 7) == 0)
1498 if (
png_muldiv(&right, xy->redx-xy->bluex, xy->whitey-xy->bluey, 7) == 0)
1500 if (
png_muldiv(&green_inverse, xy->whitey, denominator, left-right) == 0 ||
1501 green_inverse <= xy->whitey)
1509 if (blue_scale <= 0)
1527 green_inverse) == 0)
◆ png_XYZ_normalize()
| static int png_XYZ_normalize |
( |
png_XYZ * |
XYZ | ) |
|
|
static |
1546 if (
XYZ->red_Y < 0 ||
XYZ->green_Y < 0 ||
XYZ->blue_Y < 0 ||
1547 XYZ->red_X < 0 ||
XYZ->green_X < 0 ||
XYZ->blue_X < 0 ||
1548 XYZ->red_Z < 0 ||
XYZ->green_Z < 0 ||
XYZ->blue_Z < 0)
1557 if (0x7fffffff - Y < XYZ->
green_X)
1560 if (0x7fffffff - Y < XYZ->
blue_X)
◆ png_colorspace_endpoints_match()
| static int png_colorspace_endpoints_match |
( |
const png_xy * |
xy1, |
|
|
const png_xy * |
xy2, |
|
|
int |
delta |
|
) |
| |
|
static |
◆ png_colorspace_check_xy()
| static int png_colorspace_check_xy |
( |
png_XYZ * |
XYZ, |
|
|
const png_xy * |
xy |
|
) |
| |
|
static |
◆ png_colorspace_check_XYZ()
| static int png_colorspace_check_XYZ |
( |
png_xy * |
xy, |
|
|
png_XYZ * |
XYZ |
|
) |
| |
|
static |
◆ png_colorspace_set_xy_and_XYZ()
| static int png_colorspace_set_xy_and_XYZ |
( |
png_const_structrp |
png_ptr, |
|
|
png_colorspacerp |
colorspace, |
|
|
const png_xy * |
xy, |
|
|
const png_XYZ * |
XYZ, |
|
|
int |
preferred |
|
) |
| |
|
static |
1676 if ((colorspace->flags & PNG_COLORSPACE_INVALID) != 0)
1683 if (preferred < 2 &&
1684 (colorspace->flags & PNG_COLORSPACE_HAVE_ENDPOINTS) != 0)
1692 colorspace->flags |= PNG_COLORSPACE_INVALID;
1702 colorspace->end_points_xy = *xy;
1703 colorspace->end_points_XYZ = *
XYZ;
1704 colorspace->flags |= PNG_COLORSPACE_HAVE_ENDPOINTS;
1710 colorspace->flags |= PNG_COLORSPACE_ENDPOINTS_MATCH_sRGB;
1713 colorspace->flags &= PNG_COLORSPACE_CANCEL(
1714 PNG_COLORSPACE_ENDPOINTS_MATCH_sRGB);
◆ png_colorspace_set_chromaticities()
| int png_colorspace_set_chromaticities |
( |
png_const_structrp |
png_ptr, |
|
|
png_colorspacerp |
colorspace, |
|
|
const png_xy * |
xy, |
|
|
int |
preferred |
|
) |
| |
1741 colorspace->flags |= PNG_COLORSPACE_INVALID;
1749 colorspace->flags |= PNG_COLORSPACE_INVALID;
◆ png_colorspace_set_endpoints()
| int png_colorspace_set_endpoints |
( |
png_const_structrp |
png_ptr, |
|
|
png_colorspacerp |
colorspace, |
|
|
const png_XYZ * |
XYZ_in, |
|
|
int |
preferred |
|
) |
| |
1760 png_XYZ
XYZ = *XYZ_in;
1771 colorspace->flags |= PNG_COLORSPACE_INVALID;
1776 colorspace->flags |= PNG_COLORSPACE_INVALID;
◆ png_icc_tag_char()
1789 if (
byte >= 32 &&
byte <= 126)
◆ png_icc_tag_name()
◆ is_ICC_signature_char()
1809 return it == 32 || (it >= 48 && it <= 57) || (it >= 65 && it <= 90) ||
1810 (it >= 97 && it <= 122);
◆ is_ICC_signature()
◆ png_icc_profile_error()
1829 if (colorspace !=
NULL)
1830 colorspace->flags |= PNG_COLORSPACE_INVALID;
1832 pos =
png_safecat(message, (
sizeof message), 0,
"profile '");
1834 pos =
png_safecat(message, (
sizeof message), pos,
"': ");
1840 message[pos++] =
':';
1841 message[pos++] =
' ';
1843 # ifdef PNG_WARNINGS_SUPPORTED
1851 pos =
png_safecat(message, (
sizeof message), pos,
"h: ");
1855 pos =
png_safecat(message, (
sizeof message), pos, reason);
◆ png_colorspace_set_sRGB()
| int png_colorspace_set_sRGB |
( |
png_const_structrp |
png_ptr, |
|
|
png_colorspacerp |
colorspace, |
|
|
int |
intent |
|
) |
| |
1887 static const png_XYZ sRGB_XYZ =
1891 35758, 71517, 11919,
1896 if ((colorspace->flags & PNG_COLORSPACE_INVALID) != 0)
1912 if ((colorspace->flags & PNG_COLORSPACE_HAVE_INTENT) != 0 &&
1913 colorspace->rendering_intent !=
intent)
1917 if ((colorspace->flags & PNG_COLORSPACE_FROM_sRGB) != 0)
1926 if ((colorspace->flags & PNG_COLORSPACE_HAVE_ENDPOINTS) != 0 &&
1940 colorspace->flags |= PNG_COLORSPACE_HAVE_INTENT;
1943 colorspace->end_points_xy =
sRGB_xy;
1944 colorspace->end_points_XYZ = sRGB_XYZ;
1945 colorspace->flags |=
1946 (PNG_COLORSPACE_HAVE_ENDPOINTS|PNG_COLORSPACE_ENDPOINTS_MATCH_sRGB);
1950 colorspace->flags |= PNG_COLORSPACE_HAVE_GAMMA;
1953 colorspace->flags |=
1954 (PNG_COLORSPACE_MATCHES_sRGB|PNG_COLORSPACE_FROM_sRGB);
◆ icc_check_length()
1973 if (profile_length < 132)
◆ png_icc_check_length()
1993 # ifdef PNG_SET_USER_LIMITS_SUPPORTED
1994 else if (
png_ptr->user_chunk_malloc_max > 0 &&
1995 png_ptr->user_chunk_malloc_max < profile_length)
1997 "exceeds application limits");
1998 # elif PNG_USER_CHUNK_MALLOC_MAX > 0
2001 "exceeds libpng limits");
2006 "exceeds system limits");
◆ png_icc_check_header()
2026 if (temp != profile_length)
2028 "length does not match profile");
2031 if (temp > 3 && (profile_length & 3))
2036 if (temp > 357913930 ||
2037 profile_length < 132+12*temp)
2039 "tag count too large");
2047 "invalid rendering intent");
2054 "intent outside defined range");
2069 if (temp != 0x61637370)
2071 "invalid signature");
2082 "PCS illuminant is not D50");
2110 "RGB color space not permitted on grayscale PNG");
2116 "Gray color space not permitted on RGB PNG");
2121 "invalid ICC profile color space");
2146 "invalid embedded Abstract ICC profile");
2156 "unexpected DeviceLink ICC profile class");
2164 "unexpected NamedColor ICC profile class");
2174 "unrecognized ICC profile class");
2190 "unexpected ICC PCS encoding");
◆ png_icc_check_tag_table()
2208 for (itag=0; itag < tag_count; ++itag, tag += 12)
2224 if (tag_start > profile_length || tag_length > profile_length - tag_start)
2226 "ICC profile tag outside profile");
2228 if ((tag_start & 3) != 0)
2235 "ICC profile tag start not a multiple of 4");
◆ png_compare_ICC_profile_with_sRGB()
2320 #if PNG_sRGB_PROFILE_CHECKS > 1
2325 #ifdef PNG_SET_OPTION_SUPPORTED
2343 # if PNG_sRGB_PROFILE_CHECKS == 0
2372 # if PNG_sRGB_PROFILE_CHECKS > 1
2402 "out-of-date sRGB profile with no signature",
2410 # if PNG_sRGB_PROFILE_CHECKS > 0
2416 "Not recognizing known sRGB profile that has been edited",
◆ png_icc_set_sRGB()
◆ png_colorspace_set_ICC()
2446 if ((colorspace->flags & PNG_COLORSPACE_INVALID) != 0)
2455 # if defined(PNG_sRGB_SUPPORTED) && PNG_sRGB_PROFILE_CHECKS >= 0
◆ png_colorspace_set_rgb_coefficients()
2472 if (
png_ptr->rgb_to_gray_coefficients_set == 0 &&
2473 (
png_ptr->colorspace.flags & PNG_COLORSPACE_HAVE_ENDPOINTS) != 0)
2484 r >= 0 &&
png_muldiv(&r, r, 32768, total) && r >= 0 && r <= 32768 &&
2485 g >= 0 &&
png_muldiv(&g, g, 32768, total) && g >= 0 && g <= 32768 &&
2498 else if (r+g+
b < 32768)
2503 if (g >= r && g >=
b)
2505 else if (r >= g && r >=
b)
2514 "internal error handling cHRM coefficients");
◆ png_check_IHDR()
2589 #ifdef PNG_SET_USER_LIMITS_SUPPORTED
2611 #ifdef PNG_SET_USER_LIMITS_SUPPORTED
2612 if (height >
png_ptr->user_height_max)
2622 if (bit_depth != 1 && bit_depth != 2 && bit_depth != 4 &&
2623 bit_depth != 8 && bit_depth != 16)
2629 if (color_type < 0 || color_type == 1 ||
2630 color_type == 5 || color_type > 6)
2657 #ifdef PNG_MNG_FEATURES_SUPPORTED
2668 png_ptr->mng_features_permitted != 0)
◆ png_check_fp_number()
2715 int state = *statep;
2716 size_t i = *whereami;
2728 case 49:
case 50:
case 51:
case 52:
2729 case 53:
case 54:
case 55:
case 56:
2733 default:
goto PNG_FP_End;
2819 default:
goto PNG_FP_End;
◆ png_check_fp_string()
2842 size_t char_index=0;
2845 (char_index ==
size ||
string[char_index] == 0))
◆ png_pow10()
| static double png_pow10 |
( |
int |
power | ) |
|
|
static |
2868 if (power < DBL_MIN_10_EXP)
return 0;
2869 recip = 1; power = -power;
2878 if (power & 1) d *= mult;
2884 if (recip != 0) d = 1/d;
◆ png_ascii_from_fp()
2912 precision = DBL_DIG;
2915 if (precision > DBL_DIG+1)
2916 precision = DBL_DIG+1;
2919 if (
size >= precision+5)
2928 if (fp >= DBL_MIN && fp <= DBL_MAX)
2942 (
void)frexp(fp, &exp_b10);
2944 exp_b10 = (exp_b10 * 77) >> 8;
2949 while (base < DBL_MIN || base < fp)
2954 if (test <= DBL_MAX)
2956 ++exp_b10; base = test;
2973 fp /= 10; ++exp_b10;
2983 unsigned int czero, clead, cdigits;
2989 if (exp_b10 < 0 && exp_b10 > -3)
3013 if (cdigits+czero+1 < precision+clead)
3026 if (cdigits == 0) --clead;
3030 while (cdigits > 0 && d > 9)
3034 if (exp_b10 != (-1))
3039 ch = *--ascii; ++
size;
3057 if (exp_b10 == (-1))
3067 ++
size; exp_b10 = 1;
3088 if (cdigits == 0) ++clead;
3093 cdigits += czero - clead;
3102 if (exp_b10 != (-1))
3106 *ascii++ = 46; --
size;
3111 *ascii++ = 48; --czero;
3114 if (exp_b10 != (-1))
3118 *ascii++ = 46; --
size;
3123 *ascii++ = (char)(48 + (
int)d); ++cdigits;
3126 while (cdigits+czero < precision+clead && fp > DBL_MIN);
3137 if (exp_b10 >= (-1) && exp_b10 <= 2)
3146 while (exp_b10-- > 0) *ascii++ = 48;
3164 *ascii++ = 69; --
size;
3171 unsigned int uexp_b10;
3175 *ascii++ = 45; --
size;
3176 uexp_b10 = 0U-exp_b10;
3180 uexp_b10 = 0U+exp_b10;
3184 while (uexp_b10 > 0)
3186 exponent[cdigits++] = (char)(48 + uexp_b10 % 10);
3196 while (cdigits > 0) *ascii++ = exponent[--cdigits];
3204 else if (!(fp >= DBL_MIN))
◆ png_ascii_from_fixed()
3251 if (num <= 0x80000000)
3253 unsigned int ndigits = 0, first = 16 ;
3259 unsigned int tmp = num/10;
3261 digits[ndigits++] = (char)(48 + num);
3265 if (first == 16 && num > 0)
3272 while (ndigits > 5) *ascii++ = digits[--ndigits];
3289 while (ndigits >= first) *ascii++ = digits[--ndigits];
◆ png_fixed()
3318 double r = floor(100000 * fp + .5);
3320 if (r > 2147483647. || r < -2147483648.)
3321 png_fixed_error(
png_ptr, text);
3323 # ifndef PNG_ERROR_TEXT_SUPPORTED
◆ png_muldiv()
3355 if (
a == 0 || times == 0)
3362 #ifdef PNG_FLOATING_ARITHMETIC_SUPPORTED
3369 if (r <= 2147483647. && r >= -2147483648.)
3380 negative = 1,
A = -
a;
3385 negative = !negative, T = -times;
3390 negative = !negative, D = -divisor;
3397 s16 = (
A >> 16) * (T & 0xffff) +
3398 (
A & 0xffff) * (T >> 16);
3402 s32 = (
A >> 16) * (T >> 16) + (s16 >> 16);
3403 s00 = (
A & 0xffff) * (T & 0xffff);
3405 s16 = (s16 & 0xffff) << 16;
3420 while (--bitshift >= 0)
3425 d32 = D >> (32-bitshift), d00 = D << bitshift;
3432 if (s00 < d00) --s32;
3433 s32 -= d32, s00 -= d00, result += 1<<bitshift;
3437 if (s32 == d32 && s00 >= d00)
3438 s32 = 0, s00 -= d00, result += 1<<bitshift;
3442 if (s00 >= (D >> 1))
3449 if ((negative != 0 && result <= 0) ||
3450 (negative == 0 && result >= 0))
◆ png_muldiv_warn()
◆ png_reciprocal()
3490 #ifdef PNG_FLOATING_ARITHMETIC_SUPPORTED
3491 double r = floor(1E10/
a+.5);
3493 if (r <= 2147483647. && r >= -2147483648.)
◆ png_gamma_significant()
◆ png_product2()
3523 #ifdef PNG_FLOATING_ARITHMETIC_SUPPORTED
3524 double r =
a * 1E-5;
3528 if (r <= 2147483647. && r >= -2147483648.)
◆ png_reciprocal2()
3546 #ifdef PNG_FLOATING_ARITHMETIC_SUPPORTED
3547 if (
a != 0 &&
b != 0)
3553 if (r <= 2147483647. && r >= -2147483648.)
◆ png_gamma_8bit_correct()
| png_byte png_gamma_8bit_correct |
( |
unsigned int |
value, |
|
|
png_fixed_point |
gamma_val |
|
) |
| |
3866 if (value > 0 && value < 255)
3868 # ifdef PNG_FLOATING_ARITHMETIC_SUPPORTED
3893 double r = floor(255*pow((
int)value/255.,gamma_val*.00001)+.5);
3900 return png_exp8bit(res);
3907 return (png_byte)(value & 0xff);
◆ png_gamma_16bit_correct()
3914 if (value > 0 && value < 65535)
3916 # ifdef PNG_FLOATING_ARITHMETIC_SUPPORTED
3922 double r = floor(65535*pow((
png_int_32)value/65535.,
3923 gamma_val*.00001)+.5);
3930 return png_exp16bit(res);
◆ png_gamma_correct()
3953 #ifdef PNG_16BIT_SUPPORTED
◆ png_build_16bit_table()
3976 unsigned int num = 1U << (8U - shift);
3977 #ifdef PNG_FLOATING_ARITHMETIC_SUPPORTED
3981 double fmax = 1.0 / (((
png_int_32)1 << (16U - shift)) - 1);
3983 unsigned int max = (1U << (16U - shift)) - 1U;
3984 unsigned int max_by_2 = 1U << (15U - shift);
3990 for (
i = 0;
i < num;
i++)
4009 for (j = 0; j < 256; j++)
4012 # ifdef PNG_FLOATING_ARITHMETIC_SUPPORTED
4017 double d = floor(65535.*pow(ig*fmax, gamma_val*.00001)+.5);
4021 ig = (ig * 65535U + max_by_2)/
max;
4032 for (j = 0; j < 256; j++)
4037 ig = (ig * 65535U + max_by_2)/
max;
◆ png_build_16to8_table()
4052 unsigned int num = 1U << (8U - shift);
4053 unsigned int max = (1U << (16U - shift))-1U;
4064 for (
i = 0;
i < num;
i++)
4085 for (
i = 0;
i < 255; ++
i)
4094 bound = (bound *
max + 32768U)/65535U + 1U;
4096 while (last < bound)
4098 table[last & (0xffU >> shift)][last >> (8U - shift)] = out;
4104 while (last < (num << 8))
4106 table[last & (0xff >> shift)][last >> (8U - shift)] = 65535U;
◆ png_build_8bit_table()
4124 for (
i=0;
i<256;
i++)
4128 for (
i=0;
i<256; ++
i)
4129 table[
i] = (png_byte)(
i & 0xff);
◆ png_destroy_gamma_table()
4141 #ifdef PNG_16BIT_SUPPORTED
4145 int istop = (1 << (8 -
png_ptr->gamma_shift));
4146 for (
i = 0;
i < istop;
i++)
4155 #if defined(PNG_READ_BACKGROUND_SUPPORTED) || \
4156 defined(PNG_READ_ALPHA_MODE_SUPPORTED) || \
4157 defined(PNG_READ_RGB_TO_GRAY_SUPPORTED)
4163 #ifdef PNG_16BIT_SUPPORTED
4167 int istop = (1 << (8 -
png_ptr->gamma_shift));
4168 for (
i = 0;
i < istop;
i++)
4178 int istop = (1 << (8 -
png_ptr->gamma_shift));
4179 for (
i = 0;
i < istop;
i++)
◆ png_build_gamma_table()
4198 png_debug(1,
"in png_build_gamma_table");
4219 #if defined(PNG_READ_BACKGROUND_SUPPORTED) || \
4220 defined(PNG_READ_ALPHA_MODE_SUPPORTED) || \
4221 defined(PNG_READ_RGB_TO_GRAY_SUPPORTED)
4234 #ifdef PNG_16BIT_SUPPORTED
4237 png_byte shift, sig_bit;
4241 sig_bit =
png_ptr->sig_bit.red;
4243 if (
png_ptr->sig_bit.green > sig_bit)
4244 sig_bit =
png_ptr->sig_bit.green;
4246 if (
png_ptr->sig_bit.blue > sig_bit)
4247 sig_bit =
png_ptr->sig_bit.blue;
4250 sig_bit =
png_ptr->sig_bit.gray;
4270 if (sig_bit > 0 && sig_bit < 16U)
4272 shift = (png_byte)((16U - sig_bit) & 0xff);
4307 #if defined(PNG_READ_BACKGROUND_SUPPORTED) || \
4308 defined(PNG_READ_ALPHA_MODE_SUPPORTED) || \
4309 defined(PNG_READ_RGB_TO_GRAY_SUPPORTED)
◆ png_set_option()
4338 png_uint_32 setting = (2U + (onoff != 0)) << option;
4343 return (
int)(current & mask) >> option;
◆ png_image_free_function()
| static int png_image_free_function |
( |
png_voidp |
argument | ) |
|
|
static |
4535 # ifdef PNG_STDIO_SUPPORTED
4562 # ifdef PNG_SIMPLIFIED_WRITE_SUPPORTED
4570 # ifdef PNG_SIMPLIFIED_READ_SUPPORTED
◆ png_image_free()
◆ png_image_error()
◆ sRGB_xy
Initial value:=
{
64000, 33000,
30000, 60000,
15000, 6000,
31270, 32900
}
◆ D50_nCIEXYZ
| const png_byte D50_nCIEXYZ[12] |
|
static |
Initial value:=
{ 0x00, 0x00, 0xf6, 0xd6, 0x00, 0x01, 0x00, 0x00, 0x00, 0x00, 0xd3, 0x2d }
◆ adler
◆ crc
◆ length
◆ md5
◆ have_md5
◆ is_broken
◆ intent
◆ png_sRGB_checks
| const { ... } png_sRGB_checks[] |
◆ png_sRGB_table
◆ png_sRGB_base
◆ png_sRGB_delta
| const png_byte png_sRGB_delta[512] |
#define Z_MEM_ERROR
Definition: zlib.h:183
#define PNG_FP_WAS_VALID
Definition: pngpriv.h:1912
#define PNG_SCALE_16_TO_8
Definition: pngpriv.h:669
z_stream zstream
Definition: pngstruct.h:183
png_uint_32 adler
Definition: png.c:2247
const char items[11][6]
Definition: window_list.c:5
png_uint_32 crc
Definition: png.c:2247
#define PNG_FREE_TRNS
Definition: png.h:1759
const typedef png_byte * png_const_bytep
Definition: pngconf.h:580
#define PNG_CHUNK_ANCILLARY(c)
Definition: pngpriv.h:897
#define PNG_INTERLACE_LAST
Definition: png.h:689
#define PNG_FREE_ROWS
Definition: png.h:1751
#define png_fp_add(state, flags)
Definition: png.c:2708
#define PNG_FREE_SPLT
Definition: png.h:1750
void PNGAPI png_destroy_read_struct(png_structpp png_ptr_ptr, png_infopp info_ptr_ptr, png_infopp end_info_ptr_ptr)
Definition: pngread.c:1005
int png_safe_execute(png_imagep image_in, int(*function)(png_voidp), png_voidp arg)
Definition: pngerror.c:936
#define PNG_16_TO_8
Definition: pngpriv.h:652
png_fixed_point png_reciprocal(png_fixed_point a)
Definition: png.c:3488
static void png_icc_tag_name(char *name, png_uint_32 tag)
Definition: png.c:1796
#define PNG_UNUSED(param)
Definition: pngpriv.h:438
#define Z_ERRNO
Definition: zlib.h:180
#define PNG_DESTROY_WILL_FREE_DATA
Definition: png.h:1744
bool error
Definition: auto_build.py:637
#define Z_BUF_ERROR
Definition: zlib.h:184
#define PNG_FREE_HIST
Definition: png.h:1748
static void png_build_16bit_table(png_structrp png_ptr, png_uint_16pp *ptable, unsigned int shift, png_fixed_point gamma_val)
Definition: png.c:3972
#define PNG_UINT_31_MAX
Definition: png.h:649
static int png_compare_ICC_profile_with_sRGB(png_const_structrp png_ptr, png_const_bytep profile, uLong adler)
Definition: png.c:2307
void * png_voidp
Definition: pngconf.h:577
#define PNG_INFO_tRNS
Definition: png.h:736
unsigned long uLong
Definition: zconf.h:394
#define PNG_OPTION_ON
Definition: png.h:3217
void PNGAPI png_free(png_const_structrp png_ptr, png_voidp ptr)
Definition: pngmem.c:232
#define PNG_INFO_pCAL
Definition: png.h:742
#define PNG_FP_SAW_ANY
Definition: pngpriv.h:1908
free_func zfree
Definition: zlib.h:99
void PNGAPI png_set_mem_fn(png_structrp png_ptr, png_voidp mem_ptr, png_malloc_ptr malloc_fn, png_free_ptr free_fn)
Definition: pngmem.c:260
static double png_pow10(int power)
Definition: png.c:2858
#define Z_DATA_ERROR
Definition: zlib.h:182
#define PNG_UNEXPECTED_ZLIB_RETURN
Definition: pngpriv.h:973
static const struct @58 png_sRGB_checks[]
#define PNG_FREE_SCAL
Definition: png.h:1753
png_info *PNG_RESTRICT png_inforp
Definition: png.h:471
uint8_t type
Definition: UsbCore.h:184
start
Definition: g29_auto.py:150
#define PNG_LIBPNG_VER
Definition: png.h:321
png_uint_32 warning_or_error
Definition: png.h:2704
#define PNG_COMPOSE
Definition: pngpriv.h:649
#define Z_STREAM_ERROR
Definition: zlib.h:181
#define PNG_IS_READ_STRUCT
Definition: pngpriv.h:639
#define PNG_MAX_GAMMA_8
Definition: pnglibconf.h:201
#define PNG_FP_FRACTION
Definition: pngpriv.h:1901
char message[64]
Definition: png.h:2706
png_byte * png_bytep
Definition: pngconf.h:579
#define Z_NEED_DICT
Definition: zlib.h:179
uint8_t i
Definition: screen_test_graph.c:72
Definition: L6470_Marlin.h:30
#define PNG_INFO_PLTE
Definition: png.h:735
unsigned long ZEXPORT crc32(unsigned long crc, const unsigned char FAR *buf, uInt len)
Definition: crc32.c:237
#define max(a, b)
Definition: wiring_constants.h:40
static volatile fsensor_t state
Definition: filament_sensor.c:23
static int png_colorspace_check_XYZ(png_xy *xy, png_XYZ *XYZ)
Definition: png.c:1644
const typedef png_struct *PNG_RESTRICT png_const_structrp
Definition: png.h:470
#define PNG_FREE_ALL
Definition: png.h:1762
#define PNG_COLOR_TYPE_RGB_ALPHA
Definition: png.h:671
unsigned int for_write
Definition: pngpriv.h:2044
png_const_charp PNGAPI png_get_header_ver(png_const_structrp png_ptr)
Definition: png.c:844
#define A(CODE)
Definition: macros.h:75
png_const_structrp png_const_inforp int png_fixed_point * width
Definition: png.h:2161
#define PNG_FILTER_TYPE_BASE
Definition: png.h:682
#define PNG_FLAG_CRC_CRITICAL_IGNORE
Definition: pngpriv.h:690
#define png_fp_set(state, value)
Definition: png.c:2709
#define PNG_SIZE_MAX
Definition: png.h:651
#define PNG_FP_SAW_E
Definition: pngpriv.h:1907
void PNGAPI png_destroy_write_struct(png_structpp png_ptr_ptr, png_infopp info_ptr_ptr)
Definition: pngwrite.c:983
#define PNG_INTRAPIXEL_DIFFERENCING
Definition: png.h:683
png_byte is_broken
Definition: png.c:2250
#define PNG_FP_SAW_SIGN
Definition: pngpriv.h:1904
#define png_voidcast(type, value)
Definition: pngpriv.h:494
#define NULL
Definition: usbd_def.h:53
#define XYZ
Definition: macros.h:27
png_structrp png_ptr
Definition: png.h:1083
int png_check_fp_number(png_const_charp string, size_t size, int *statep, png_size_tp whereami)
Definition: png.c:2712
#define PNG_COLOR_TYPE_RGB
Definition: png.h:670
png_const_structrp png_const_inforp info_ptr
Definition: png.h:1939
#define PNG_FLAG_MNG_FILTER_64
Definition: png.h:858
#define PNG_NUMBER_BUFFER_SIZE
Definition: pngpriv.h:1752
int png_user_version_check(png_structrp png_ptr, png_const_charp user_png_ver)
Definition: png.c:193
#define PNG_INFO_gAMA
Definition: png.h:732
static int png_image_free_function(png_voidp argument)
Definition: png.c:4522
unsigned int png_uint_32
Definition: pngconf.h:511
#define PNG_USER_WILL_FREE_DATA
Definition: png.h:1746
#define PNG_INFO_eXIf
Definition: png.h:748
void PNGAPI png_image_free(png_imagep image)
Definition: png.c:4582
#define Z_NULL
Definition: zlib.h:212
png_uint_16(PNGAPI png_get_uint_16)(png_const_bytep buf)
Definition: pngrutil.c:102
#define PNG_NUMBER_FORMAT_u
Definition: pngpriv.h:1757
#define PNG_FREE_EXIF
Definition: png.h:1761
#define PNG_USER_CHUNK_MALLOC_MAX
Definition: pnglibconf.h:208
#define PNG_FLAG_CRC_ANCILLARY_USE
Definition: pngpriv.h:687
#define PNG_OPTION_INVALID
Definition: png.h:3215
#define PNG_FREE_ICCP
Definition: png.h:1749
#define APPEND_STRING(string)
#define PNGZ_MSG_CAST(s)
Definition: pngstruct.h:40
#define PNG_NUMBER_FORMAT_02u
Definition: pngpriv.h:1758
void png_chunk_report(png_const_structrp png_ptr, png_const_charp message, int error)
Definition: pngerror.c:531
png_const_structrp png_const_inforp double double double double double double double * blue_X
Definition: png.h:1939
#define PNG_FREE_PLTE
Definition: png.h:1758
static int png_icc_profile_error(png_const_structrp png_ptr, png_colorspacerp colorspace, png_const_charp name, png_alloc_size_t value, png_const_charp reason)
Definition: png.c:1823
#define PNG_INFO_sRGB
Definition: png.h:743
void PNGAPI png_benign_error(png_const_structrp png_ptr, png_const_charp error_message)
Definition: pngerror.c:362
png_byte blue
Definition: png.h:482
#define png_debug(l, m)
Definition: pngdebug.h:145
#define PNG_FP_EXPONENT
Definition: pngpriv.h:1902
png_byte green
Definition: png.h:481
void PNGAPI png_free_data(png_const_structrp png_ptr, png_inforp info_ptr, png_uint_32 mask, int num)
Definition: png.c:471
void png_icc_set_sRGB(png_const_structrp png_ptr, png_colorspacerp colorspace, png_const_bytep profile, uLong adler)
Definition: png.c:2428
png_byte png_gamma_8bit_correct(unsigned int value, png_fixed_point gamma_val)
Definition: png.c:3864
void
Definition: png.h:1083
int png_muldiv(png_fixed_point_p res, png_fixed_point a, png_int_32 times, png_int_32 divisor)
Definition: png.c:3349
png_int_32 png_fixed_point
Definition: pngconf.h:574
const typedef char * png_const_charp
Definition: pngconf.h:590
#define PNG_COMPRESSION_TYPE_BASE
Definition: png.h:678
png_const_structrp png_const_inforp double double double double * green_X
Definition: png.h:1939
#define Z_OK
Definition: zlib.h:177
png_struct *PNG_RESTRICT png_structrp
Definition: png.h:469
void png_colorspace_sync_info(png_const_structrp png_ptr, png_inforp info_ptr)
Definition: png.c:1169
#define PNG_USER_HEIGHT_MAX
Definition: pnglibconf.h:209
static int is_ICC_signature(png_alloc_size_t it)
Definition: png.c:1814
unsigned int owned_file
Definition: pngpriv.h:2045
static int png_colorspace_endpoints_match(const png_xy *xy1, const png_xy *xy2, int delta)
Definition: png.c:1592
#define PNG_SKIP_sRGB_CHECK_PROFILE
Definition: png.h:3203
Definition: pngpriv.h:2035
alloc_func zalloc
Definition: zlib.h:98
#define PNG_INFO_sCAL
Definition: png.h:746
#define PNG_FREE_TEXT
Definition: png.h:1760
png_voidp error_buf
Definition: pngpriv.h:2039
#define PNG_HANDLE_CHUNK_AS_DEFAULT
Definition: png.h:2345
#define APPEND_NUMBER(format, value)
png_uint_16 png_gamma_16bit_correct(unsigned int value, png_fixed_point gamma_val)
Definition: png.c:3912
list a
Definition: createSpeedLookupTable.py:29
static const png_byte D50_nCIEXYZ[12]
Definition: png.c:1966
static void png_build_8bit_table(png_structrp png_ptr, png_bytepp ptable, png_fixed_point gamma_val)
Definition: png.c:4117
#define png_get_uint_32(buf)
Definition: png.h:2598
#define Z_STREAM_END
Definition: zlib.h:178
static char png_icc_tag_char(png_uint_32 byte)
Definition: png.c:1786
#define PNG_INFO_sPLT
Definition: png.h:745
Definition: pngstruct.h:143
int png_icc_check_header(png_const_structrp png_ptr, png_colorspacerp colorspace, png_const_charp name, png_uint_32 profile_length, png_const_bytep profile, int color_type)
Definition: png.c:2014
png_uint_16 ** png_uint_16pp
Definition: pngconf.h:609
#define PNG_CHUNK_WARNING
Definition: pngpriv.h:1842
#define PNG_RGB_TO_GRAY
Definition: pngpriv.h:665
png_byte have_md5
Definition: png.c:2249
int PNGAPI png_handle_as_unknown(png_const_structrp png_ptr, png_const_bytep chunk_name)
Definition: png.c:926
#define PNG_IMAGE_ERROR
Definition: png.h:2692
else png_error(png_ptr, "png_image_write_to_memory: PNG too big")
png_uint_16 * png_uint_16p
Definition: pngconf.h:585
png_voidp io_ptr
Definition: pngstruct.h:158
png_fixed_point png_reciprocal2(png_fixed_point a, png_fixed_point b)
Definition: png.c:3543
#define PNG_USER_CHUNK_CACHE_MAX
Definition: pnglibconf.h:207
#define PNG_LIBPNG_VER_STRING
Definition: png.h:280
static int png_XYZ_from_xy(png_XYZ *XYZ, const png_xy *xy)
Definition: png.c:1276
#define PNG_CHUNK_WRITE_ERROR
Definition: pngpriv.h:1843
static int png_colorspace_check_xy(png_XYZ *XYZ, const png_xy *xy)
Definition: png.c:1618
#define PNG_FP_STATE
Definition: pngpriv.h:1903
static const png_xy sRGB_xy
Definition: png.c:1662
#define PNG_FP_NONZERO
Definition: pngpriv.h:1914
size_t png_alloc_size_t
Definition: pngconf.h:557
#define PNG_FLAG_CRC_ANCILLARY_NOWARN
Definition: pngpriv.h:688
#define PNG_INFO_cHRM
Definition: png.h:734
#define PNG_FREE_MUL
Definition: png.h:1763
#define Z_VERSION_ERROR
Definition: zlib.h:185
#define PNG_CHUNK_ERROR
Definition: pngpriv.h:1844
#define PNG_COLOR_MASK_COLOR
Definition: png.h:664
#define PNG_HAVE_PNG_SIGNATURE
Definition: pngpriv.h:636
#define PNG_FREE_PCAL
Definition: png.h:1752
int PNGAPI png_convert_to_rfc1123_buffer(char out[29], png_const_timep ptime)
Definition: png.c:737
static void png_build_16to8_table(png_structrp png_ptr, png_uint_16pp *ptable, unsigned int shift, png_fixed_point gamma_val)
Definition: png.c:4049
#define PNG_CSTRING_FROM_CHUNK(s, c)
Definition: pngpriv.h:893
#define PNG_FP_INTEGER
Definition: pngpriv.h:1900
png_byte red
Definition: png.h:480
void PNGAPI png_save_uint_32(png_bytep buf, png_uint_32 i)
Definition: pngwutil.c:24
int
Definition: createSpeedLookupTable.py:15
int png_gamma_significant(png_fixed_point gamma_val)
Definition: png.c:3509
int png_icc_check_tag_table(png_const_structrp png_ptr, png_colorspacerp colorspace, png_const_charp name, png_uint_32 profile_length, png_const_bytep profile)
Definition: png.c:2197
#define PNG_FLAG_LIBRARY_MISMATCH
Definition: pngpriv.h:696
void png_destroy_gamma_table(png_structrp png_ptr)
Definition: png.c:4136
#define PNG_sRGB_INTENT_LAST
Definition: png.h:719
static int png_xy_from_XYZ(png_xy *xy, const png_XYZ *XYZ)
Definition: png.c:1233
void PNGAPI png_set_error_fn(png_structrp png_ptr, png_voidp error_ptr, png_error_ptr error_fn, png_error_ptr warning_fn)
Definition: pngerror.c:835
#define PNG_GAMMA_THRESHOLD_FIXED
Definition: pnglibconf.h:194
static png_fixed_point png_product2(png_fixed_point a, png_fixed_point b)
Definition: png.c:3520
#define PNG_FLAG_CRC_ANCILLARY_MASK
Definition: pngpriv.h:711
int png_colorspace_set_sRGB(png_const_structrp png_ptr, png_colorspacerp colorspace, int intent)
Definition: png.c:1872
static int png_XYZ_normalize(png_XYZ *XYZ)
Definition: png.c:1542
unsigned int uInt
Definition: zconf.h:393
#define PNG_OPTION_NEXT
Definition: png.h:3211
#define PNG_FP_SAW_DIGIT
Definition: pngpriv.h:1905
uLong ZEXPORT adler32(uLong adler, const Bytef *buf, uInt len)
Definition: adler32.c:134
size_t png_safecat(png_charp buffer, size_t bufsize, size_t pos, png_const_charp string)
Definition: pngerror.c:112
png_uint_32 length
Definition: png.c:2247
#define PNG_INFO_hIST
Definition: png.h:738
#define PNG_FP_SAW_DOT
Definition: pngpriv.h:1906
void png_zfree(voidpf png_ptr, voidpf ptr)
Definition: png.c:118
#define PNG_FP_1
Definition: png.h:656
uint8_t byte
Definition: wiring_constants.h:112
png_infop info_ptr
Definition: pngpriv.h:2038
#define PNG_INFO_iCCP
Definition: png.h:744
voidpf opaque
Definition: zlib.h:100
#define PNG_OUT_OF_RANGE(value, ideal, delta)
Definition: pngpriv.h:766
list b
Definition: createSpeedLookupTable.py:30
#define PNG_COLOR_TYPE_GRAY_ALPHA
Definition: png.h:672
static int png_colorspace_set_xy_and_XYZ(png_const_structrp png_ptr, png_colorspacerp colorspace, const png_xy *xy, const png_XYZ *XYZ, int preferred)
Definition: png.c:1672
#define PNG_FP_NEGATIVE
Definition: pngpriv.h:1913
#define PNG_FREE_UNKN
Definition: png.h:1755
#define PNG_GAMMA_sRGB_INVERSE
Definition: pngpriv.h:906
png_structp png_ptr
Definition: pngpriv.h:2037
#define png_gt(a, b)
Definition: png.c:2543
static int png_colorspace_check_gamma(png_const_structrp png_ptr, png_colorspacerp colorspace, png_fixed_point gAMA, int from)
Definition: png.c:1070
int ZEXPORT inflateReset(z_streamp strm)
Definition: inflate.c:144
void PNGAPI png_warning(png_const_structrp png_ptr, png_const_charp warning_message)
Definition: pngerror.c:216
png_int_32(PNGAPI png_get_int_32)(png_const_bytep buf)
Definition: pngrutil.c:84
#define PNG_STRING_NEWLINE
Definition: pngdebug.h:48
#define PNG_USER_WIDTH_MAX
Definition: pnglibconf.h:210
static int icc_check_length(png_const_structrp png_ptr, png_colorspacerp colorspace, png_const_charp name, png_uint_32 profile_length)
Definition: png.c:1970
#define PNG_INFO_IDAT
Definition: png.h:747
#define PNG_NUMBER_FORMAT_x
Definition: pngpriv.h:1761
static int is_ICC_signature_char(png_alloc_size_t it)
Definition: png.c:1807
#define PNG_HEADER_VERSION_STRING
Definition: png.h:281
#define PNG_COLOR_TYPE_PALETTE
Definition: png.h:669
static png_bytep size_t size
Definition: pngwrite.c:2170
png_charp png_format_number(png_const_charp start, png_charp end, int format, png_alloc_size_t number)
Definition: pngerror.c:133
png_controlp opaque
Definition: png.h:2673
png_uint_16 intent
Definition: png.c:2251